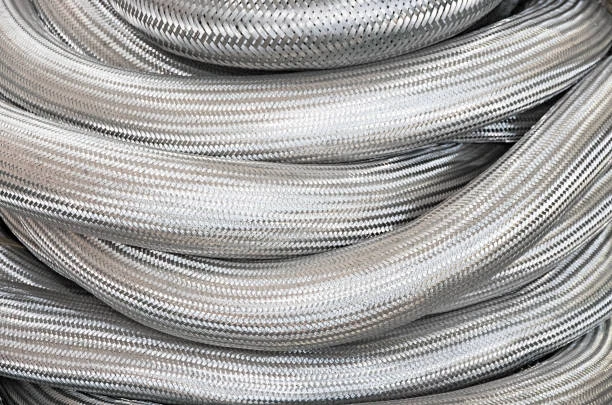
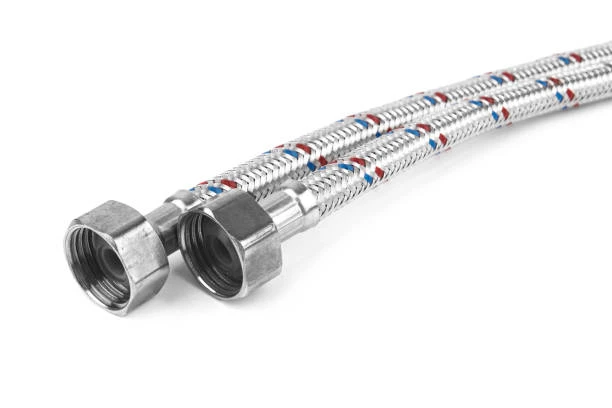
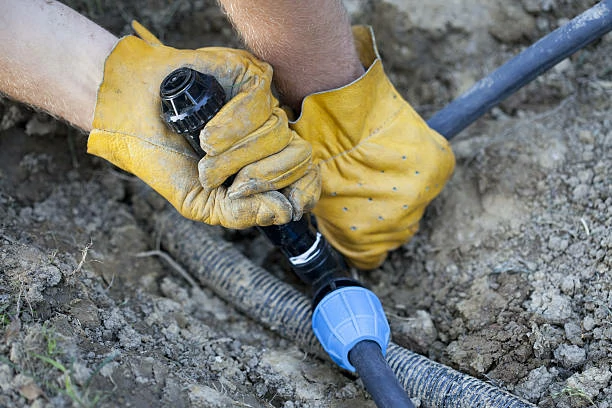
Reinforced braid hoses are the unsung heroes of modern industry and transport, providing the critical link for moving fluids and gases under high pressure with remarkable reliability. These hoses are not simple tubes; they are engineering marvels, combining flexible inner cores with incredibly strong external reinforcements, most often made from stainless steel or synthetic fibers. This construction makes them indispensable for applications where failure is not an option, from fueling an aircraft to hydraulically steering a massive ship. Their unique ability to withstand extreme pressure, resist corrosion, and maintain flexibility ensures the safe and efficient operation of countless systems that keep our world moving. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about reinforced braid hoses, from their fundamental structure to their vital role across global industries, helping you understand why they are the preferred choice for demanding transport applications.
What Are Reinforced Braid Hoses? Definition and Key Characteristics
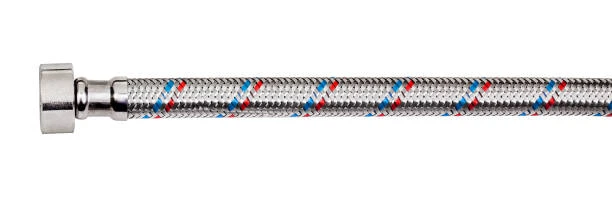
Reinforced braid hoses are flexible conduits specifically designed to transport liquids, gases, and sometimes slurries under high pressure. People often mistake them for simple pipes, but their design is far more complex and purposeful. Essentially, these hoses feature a multi-layered construction that balances flexibility with immense strength.
At the heart of the hose, we find the inner tube. This tube is made from a material compatible with the medium it carries, such as PTFE for aggressive chemicals or synthetic rubber for fuel. This inner layer ensures a smooth flow path and protects the reinforcement from degradation.
The defining feature, however, is the reinforcement layer. Manufacturers weave high-tensile strength materials over the inner tube in a braided pattern. This braid, typically crafted from stainless steel wire, aramid fiber, or polyester yarn, acts like a flexible cage. It contains the pressure within the hose, preventing it from expanding and bursting under stress. Some high-pressure applications even use multiple braid layers for added safety.
Finally, an outer cover protects this braided layer from external damage, abrasion, weather, and oil. This complete construction gives reinforced braid hoses their standout characteristics. They offer exceptional pressure resistance, far exceeding that of standard hoses. The braided structure also provides excellent impulse resilience, meaning the hose can withstand constant pressure cycles without fatiguing. Furthermore, they retain flexibility for easy routing around obstacles in tight engine compartments or industrial machinery, and manufacturers can tailor the materials to resist extreme temperatures, corrosion, and abrasion.
Common Uses and Application Industries for Reinforced Braid Hoses
The unique combination of strength and flexibility in reinforced braid hoses makes them incredibly versatile. They play a critical role in a vast array of sectors where the safe and reliable transfer of media is mission-critical. Their applications are particularly vital in the world of transportation and beyond.
In the automotive and transport industry, these hoses are absolutely essential. We find them in vehicle brake systems, handling the high hydraulic pressures that ensure safe stopping. They form part of the power steering system, allowing for easy maneuverability. In fuel injection systems, reinforced hoses transport gasoline or diesel from the tank to the engine under high pressure, improving efficiency and reducing emissions. The aerospace industry relies on them for even more critical tasks, such as fuel and hydraulic lines in aircraft, where failure is simply not an option.
The industrial manufacturing sector depends heavily on these hoses for hydraulic systems. Nearly every machine that uses hydraulic power to move—from injection molding machines and metal presses to robotic arms on an assembly line—uses reinforced braid hoses to transmit the powerful hydraulic fluid. They are also common in pneumatic systems for conducting compressed air.
Furthermore, the marine and offshore industry utilizes these hoses for their superior resistance to saltwater corrosion and harsh environments. Applications include fuel and oil transfer lines on ships, hydraulic systems for steering and winches, and even firefighting systems on board vessels.
Beyond pure transport, other industries leverage their strengths. In chemical processing plants, hoses with PTFE liners and stainless steel braiding safely transfer aggressive solvents and acids. Even in the food and beverage industry, specific reinforced hoses meeting sanitary standards handle the movement of ingredients and products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What exactly does the “braid” in a reinforced braid hose do?
The braid is the primary pressure-bearing component. When the fluid inside the hose pressurizes, it pushes outward against the hose wall. The braided layer, acting like a net, contains this expansive force. It prevents the hose from swelling and ultimately bursting, enabling it to operate safely under very high pressures that would destroy a simple rubber hose.
How do I choose between a stainless steel braid and a synthetic fiber braid?
This choice depends on your specific application needs. Stainless steel braids offer the highest level of pressure resistance and superior protection against abrasion and high temperatures. People typically use them in heavy-duty hydraulic, industrial, and automotive applications. Synthetic braids, like those made from aramid (Kevlar) or polyester, are excellent for high-pressure situations where weight reduction is important, such as in aerospace. They also provide good chemical resistance and are non-abrasive, making them suitable for sensitive environments.
Can a reinforced braid hose fail, and what are the common signs?
Yes, even these durable hoses can fail over time due to wear and tear. Common signs of impending failure include visible abrasion or wear on the outer cover, a noticeable swelling or bulge in the hose body, leaks from the inner tube seeping through the braid, and a stiff or less flexible hose that may have suffered internal damage. Regular inspection is crucial for prevention.
Are these hoses flexible enough for tight spaces?
Absolutely. While their braided construction makes them incredibly strong, it also allows them to remain highly flexible. This flexibility is a key design advantage, enabling installers to route them through cramped and complex spaces in machinery, engine bays, and industrial equipment without kinking or compromising flow.
What does the hose’s “minimum bend radius” mean, and why is it important?
The minimum bend radius is the smallest curve you can bend the hose without damaging its internal structure. Bending the hose tighter than this radius can kink the inner tube, restrict flow, and place excessive stress on the braid wires, leading to premature failure. Always follow the manufacturer’s specified bend radius to ensure hose longevity and system safety.
Conclusion
In summary, reinforced braid hoses are fundamental components that ensure safety, efficiency, and reliability in countless applications. Their sophisticated braided design transforms a simple tube into a powerful conduit capable of handling extreme pressures, temperatures, and corrosive media while maintaining crucial flexibility. From the cars we drive and the planes we fly in to the factories that build our goods and the ships that transport them, these hoses facilitate critical operations behind the scenes. Understanding their construction, capabilities, and proper maintenance is key to selecting the right hose for the job and ensuring the continuous, safe operation of the systems that depend on them. As technology advances, we can expect these essential components to evolve further, meeting even greater demands in the future of transport and industry.
IFNS’s international standards
IFNS products comply with a wide range of international standards, including ASTM 2846, DIN 8079/8080, ASTM F441/F441M SCH80, GB/T 18993 series, AS/NZS 1477, CSA B137.6, NSF/ANSI 14, and TIS 17-2532/1131-2535. These certifications ensure that our pipes and fittings meet global quality, safety, and performance requirements.
Connect
IFNS, a Chinese manufacturer with 30 years of experience, specializes in high-quality plastic pipes, fittings, and valves. Interested in IFNS’s copper fittings, copper valves, plastic pipes, or fittings? Contact us today. IFNS offers a wide range of standard pipes tailored to your needs. Explore our affordable, cost-effective valve and piping system products.
We respond to emails or faxes within 24 hours. For immediate assistance, call us anytime with questions about our products.