Introduction
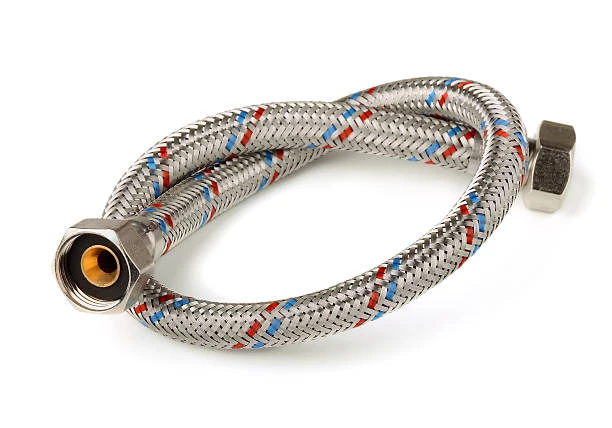
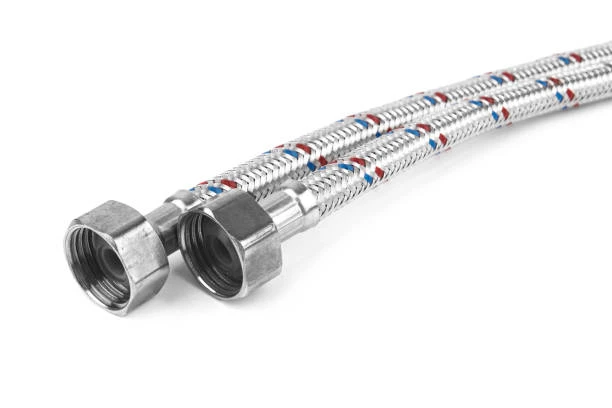
Reinforced braid hoses are critical components in industries requiring durable, flexible, and high-pressure fluid or gas transfer solutions. These hoses feature a multi-layered construction—inner tube, braided reinforcement, and protective outer cover—to withstand demanding conditions, from hydraulic systems to chemical transport. Their unique design ensures resistance to abrasion, pressure surges, and environmental factors, making them indispensable in aerospace, automotive, marine, and industrial applications. This article explores their key characteristics, diverse uses, and answers common questions to help businesses select the right hose for optimal performance.
Basic Definition and Characteristics
A reinforced braid hose consists of three primary layers:
- Inner Tube: Made from materials like rubber, PVC, or PTFE, this layer ensures compatibility with the transported medium (water, oil, chemicals, or gases).
- Reinforcement Layer: Typically woven from polyester, nylon, or stainless steel wire, this braided structure provides tensile strength and prevents bursting under pressure.
- Outer Cover: Protects against abrasion, UV exposure, and chemical corrosion, often made from synthetic rubber or thermoplastic materials.
Key Features:
- High Pressure Resistance: Steel-braided hoses support up to 6,000 PSI (hydraulic systems), while textile-reinforced variants suit lower pressures (under 1,000 PSI).
- Flexibility: Textile braids offer tight bend radii for dynamic applications, whereas steel braids balance strength and maneuverability.
- Temperature Range: Most operate between -40°C to +150°C, with specialized variants for extreme cold or heat.
- Transparency: Clear PVC or silicone hoses allow flow monitoring in food, beverage, or medical applications.
- Certifications: FDA, NSF, or REACH compliance ensures safety for food, pharmaceutical, or potable water use.
Common Uses and Industries
Reinforced braid hoses serve diverse sectors due to their adaptability and resilience. Key applications include:
1. Aerospace & Aviation
- Hydraulic & Fuel Systems: Steel-braided hoses handle extreme pressures in landing gear, brakes, and jet fuel delivery, complying with aerospace standards like AS1946.
- Engine Lubrication: Resistant to high temperatures and vibration, ensuring reliability during flight.
2. Automotive & Motorsports
- Brake & Fuel Lines: Steel braiding minimizes expansion under pressure, enhancing pedal responsiveness and fuel delivery in high-performance vehicles.
- Coolant & Oil Systems: Withstands engine heat and abrasion in race cars and heavy-duty trucks.
3. Marine & Offshore
- Bilge Pumps & Fuel Transfer: Corrosion-resistant steel or synthetic braids endure saltwater exposure in ships and offshore rigs.
- Hydraulic Steering: Provides durability in high-pressure marine systems.
4. Industrial & Manufacturing
- Hydraulic Machinery: Excavators, cranes, and presses use steel-braided hoses for power transmission under heavy loads.
- Chemical Transfer: PTFE-lined hoses safely transport acids, solvents, and volatile gases.
5. Food & Pharmaceutical
- Beverage & Dairy Lines: FDA-compliant PVC hoses transport liquids like milk and juices without contamination.
- Sterile Fluid Handling: Medical-grade silicone hoses with polyester braiding meet USP Class VI standards for labs and vaccine production.
6. HVAC & Refrigeration
- Refrigerant Lines: Steel-braided hoses manage pressure fluctuations in cooling systems and rooftop units.
- Compressed Air Systems: Reinforced hoses reduce wear in pneumatic tools and industrial air feeds.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What industries use reinforced braid hoses most?
Aerospace, automotive, marine, industrial manufacturing, and food/pharmaceutical sectors rely heavily on these hoses for high-pressure, temperature-resistant, and hygienic fluid transfer.
2. How does braiding improve hose performance?
The braided layer adds tensile strength, prevents bursting, and enhances flexibility compared to non-reinforced hoses. Steel braids excel in high-pressure systems, while textile braids suit dynamic, low-pressure applications.
3. Can reinforced hoses handle both liquids and gases?
Yes, provided the inner tube material is compatible (e.g., PTFE for chemicals, PVC for water).
4. What certifications should I check for food-grade hoses?
Look for FDA, NSF-51 (food equipment), and NSF-61 (potable water) compliance.
5. How long do reinforced braid hoses last?
Lifespan depends on usage, but steel-braided hoses typically outlast standard hoses in high-pressure environments, often lasting years with proper maintenance.
Conclusion
Reinforced braid hoses are indispensable across industries for their durability, flexibility, and resistance to extreme conditions. Their multi-layered design—inner tube, braided reinforcement, and protective cover—ensures reliable performance in hydraulic systems, chemical transfer, sterile fluid handling, and more. By understanding material options, pressure ratings, and industry-specific requirements, businesses can select hoses that optimize efficiency, safety, and longevity. Whether for aerospace hydraulics or food processing lines, these hoses deliver the strength and adaptability needed for demanding applications.